西北工业大学
材料科学与工程专业(中外合作办学)
本科生培养方案
一、专业介绍
材料是人类赖以生存的物质基础,材料科学与工程是百业之基,奠定了航空航天、海洋工程、新能源、信息技术、可再生资源、智能制造等领域科学研究和产业发展的基础,是一个涉及材料学、工程学、物理、化学等方面的宽口径、厚基础专业。伦敦玛丽女王大学材料专业是其最有影响力的学科专业之一,核心理念是围绕材料组织、结构、性能关系及材料设计、成型、应用等全流程为学生提供精英质素教育和卓越专业教育,多次被英国政府评为5星级,2011年全国学生联合会发起的调查显示其在全英排名第一。西北工业大学材料学科在国际上享有盛誉,为国家一级重点学科,2012年学科评估全国排名第三,拥有6个国家级科研与人才培养平台。
为了借鉴英国高等教育培养创新型本科人才的先进理念和模式,在本土为中国学生提供正宗的英式高等本科教育,经教育部批准,西北工业大学与伦敦玛丽女王大学进行中外合作办学,中西合璧,强强联合,成立伦敦玛丽女王大学工程学院,创办的材料科学与工程专业(080401H)充分利用两校在材料领域的优势教育资源和高水平国际合作平台,整体引进英方课程体系、教学内容、考核模式,依托双方优质师资进行合作办学,采用国际化教学模式,培养具有国际视野、通晓国际规则,具有坚实的自然科学基础、材料科学与工程专业基础和人文基础,专业竞争力强、综合素质高,能够进行跨国学习、工作并具备终生学习能力的复合型创新人才。
二、培养目标
本专业坚持以马克思主义为指导,坚持立德树人,培养具有国际视野、通晓国际规则,具有坚实的自然科学基础、材料科学与工程专业基础和人文基础,专业竞争力强、综合素质高,能够进行跨国学习、工作并具备终生学习能力的复合型创新人才。完成学业的学生有能力在世界名校深造攻读学位或就职于全球知名企业和国际组织。
(一)具备扎实的基础知识和专业技能
培养学生掌握扎实的材料科学与工程基本原理,材料制备、表征、成型,及产品设计和应用开发等方面的基础知识;掌握工程及材料科学领域的实验和计算方法;具备研究和分析金属材料、无机非金属材料、复合材料及先进功能材料的组织、结构、性能关系的能力;能够创新性地利用基础知识和专业技能专业知识进行材料研究和工程实践,具有创造性解决专业领域技术问题的能力。
(二)具备国际化能力
培养学生具有较高的英语水平,能够熟练阅读本专业英文材料、运用英文进行专业写作和技术交流;通过全英文培养模式、海外实习等途径培养学生能够获取、处理和运用信息,具备宽广的国际化视野、了解国际惯例;培养学生具有创新意识和竞争力,能够进行跨文化交流、沟通和合作;培养学生正确认识中国特色和国际比较,全面客观认识当代中国、看待外部世界。
(三)具备终身学习能力
培养学生坚持马克思主义科学理论,弘扬并践行社会主义核心价值观;正确认识时代责任和历史使命;正确认识远大抱负和脚踏实地;有高度的社会责任感、健全的人格品质、突出的交流和实践能力,具有团队合作意识、领导能力以及沟通能力;具有较强的语言组织能力和文案写作能力,能够就复杂工程与科学问题与业界同行及社会公众进行有效沟通和交流;具有工科伦理意识,以造福人类和可持续发展为理念,能够适应动态变化及时掌握材料领域的前沿知识和发展动态,在实践中持续提升自身素质。
三、培养要求
(一)基础知识掌握
要求学生掌握:材料科学领域广泛的基础知识,包括材料学、材料工程、材料结构与性能、材料加工与应用等;深入的专业知识,包括金属材料、无机非金属材料、复合材料、聚合物材料、可再生能源材料;工程及材料科学领域的实验和计算方法。
(二)专业技能培养
要求学生能够:综合运用材料科学知识与技术解决理论和实际问题,理解材料科学对工程及其他技术的重要性;制定实验方案、进行实验、分析和评估实验结果;熟悉材料实验、测试及分析设备、加工成型设备,在保证安全的前提下进行操作;检索、收集、筛选数据,准备科学和技术报告;具备材料科学与工程及相关领域科学研究、技术开发等方面的能力。
(三)综合素质培养
要求学生:具备较强的国际化能力和终身学习能力;独立自主的学习能力和工作能力;团队合作能力、领导能力以及沟通能力;对信息做出其相关性、重要性和可靠性判断的能力;了解科学对社会及全球未来的影响;具有创新意识和国际竞争力,能够进行跨文化交流、沟通和合作;具备可持续发展理念,能够适应材料领域前沿科技动态变化,在实践中持续提高自身素质。
四、学制与学位
学制:本科学制四年(4+0),按照学分制管理。
学位:学生通过全部课程并合格后,将获得西北工业大学本科毕业证书、工学学士学位证书,伦敦玛丽女王大学工学学士学位证书。
五、基本学分/学时
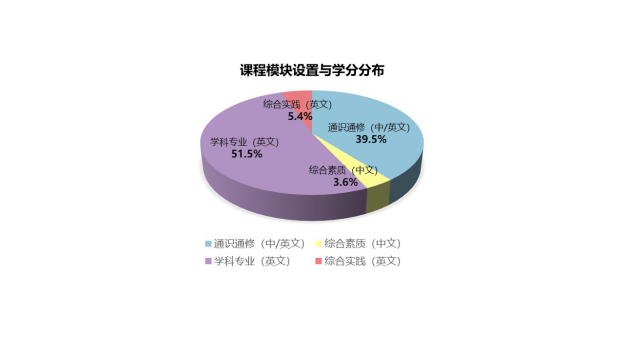
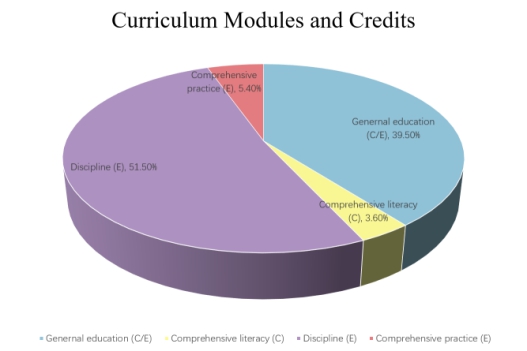
材料科学与工程专业(080401H)总学分167.0,总学时2738,包含课程模块学分分布如下:
课程模块 |
学分 |
学时 |
授课模式 |
通识通修 |
66.0 |
1122 |
中/英文 |
学科专业 |
86.0 |
1376 |
英文 |
综合素质 |
6.0 |
96 |
中文 |
综合实践 |
9.0 |
144 |
英文 |
六、学科专业课程
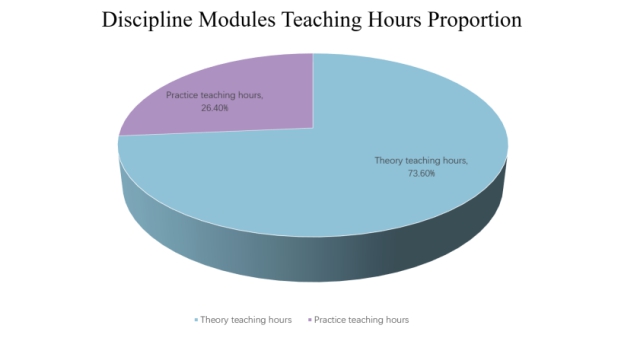
材料科学与工程专业(080401H)学科专业课程共24门,86.0学分/1376学时,包含课程如下:
1. 学科基础课程(共2门课程,7.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
NXC4012 |
工程力学 |
3.5学分 |
NXC4008 |
工程设计方法 |
3.5学分 |
2. 学科核心课程(共22门课程,79.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
QXU4000 |
材料学I-结构与性能 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4006 |
材料学II-加工与应用 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4001 |
材料分子学 |
3.5学分 |
NXC4010 |
功能材料概论 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4011 |
工程材料概论 |
4.0学分 |
QXU4007 |
材料学实验I |
3.5学分 |
QXU5017 |
材料学实验II |
3.5学分 |
NXC4022 |
热力学与相变 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5002 |
材料化学 |
4.0学分 |
QXU5010 |
表面与界面 |
3.5学分 |
NXC5015 |
结构表征 |
3.5学分 |
NXC5026 |
金属I-变形与强化 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5030 |
复合材料 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5032 |
高分子材料物理性能 |
4.0学分 |
NXC5036 |
金属II-合金与热处理 |
3.5学分 |
QXU6002 |
材料设计与选择 |
4.0学分 |
QXU6007 |
材料的环境性能 |
3.5学分 |
QXU6022 |
陶瓷 |
4.0学分 |
NXC6023 |
疲劳与蠕变 |
3.0学分 |
NXC6024 |
断裂力学 |
3.0学分 |
NXC6025 |
制造技术 |
4.0学分 |
QXU7027 |
可再生能源材料 |
3.5学分 |
七、课程模块设置与学分分布,共51门课程,167.0学分
本专业课程分为四大模块,其中:
◆通识通修模块22门课程,66.0学分/1122学时;
◆学科专业模块24门课程,86.0学分/1376学时;
◆综合素质模块最少4门课程,6.0学分/96学时;
◆综合实践2门课程,9.0学分/144学时;
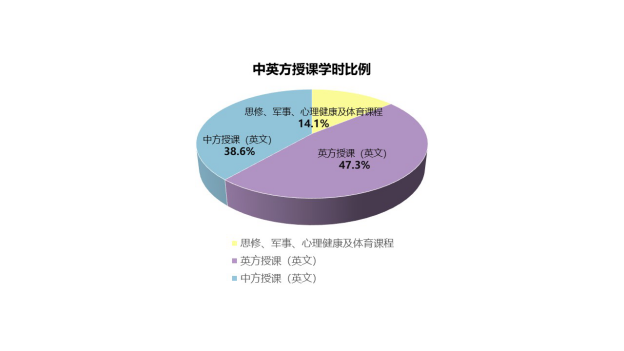
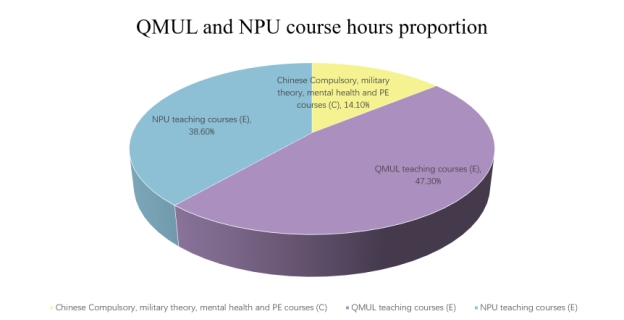
除思政、军事理论、心理健康教育和体育类课程(23.5学分)外,其余课程中由英方授课79.0学分,中方授课64.5学分,引进课程包括英语,个人发展规划、14门学科核心课程,以及毕业设计,共20门,部分满足《中华人民共和国中外合作办学条例实施办法》及教育部相关规定,即:
◆引进外方课程门数(20门)占总课程门数(51门)39.2%(超过1/3);
◆引进外方专业核心课程门数(14门)占总专业核心课程门数(22门)63.6%(超过1/3);
◆外方教师承担的专业核心课程的门数(14门)占总课程门数(51门)27.5%;
◆外方教师承担的专业核心课程的学时数(824学时)占总课程学时数(2738学时)30.1%。
(一)通识通修模块(共22门课程,66.0学分)
1. 思想政治理论课程(共5门课程,16.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
NXC2001 |
思政课I-中国近现代史纲要 |
3.0学分 |
NXC2002 |
思政课II-马克思主义基本原理 |
3.0学分 |
NXC2003 |
思政课II-思想道德修养与法律基础 |
3.0学分 |
NXC2004 |
思政课IV-毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论 |
5.0学分 |
NXC2005 |
形势与政策 |
2.0学分 |
2. 军事课程(共2门课程,3.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
U34G11002 |
军事理论 |
2.0学分 |
U34P41001 |
军事技能训练 |
1.0学分 |
3. 心理成长与个人发展课程(共1门课程,0.5学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
U34G11001 |
大学生心理健康教育 |
0.5学分 |
4.职业规划与发展课程(共3门课程,10.5学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
QXU3111 |
个人发展规划I |
3.5学分 |
QXU4111 |
个人发展规划II |
3.5学分 |
QXU5111 |
个人发展规划III |
3.5学分 |
5.公共通修基础课程(共6门课程,13.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
QXU3101 |
英语I |
3.5学分 |
QXU3102 |
英语II |
5.5学分 |
体育课第1-4学期为必修课,每学期为1学分。不同专业、不同体质、不同兴趣爱好、不同基础条件学生可以选择不同的项目。
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
U31G71001 |
体育I |
1.0学分 |
U31G71002 |
体育II |
1.0学分 |
U31G71003 |
体育III |
1.0学分 |
U31G71004 |
体育IV |
1.0学分 |
6. 分层次通修课程(共5门课程,23.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
NXC3000 |
高等数学I |
5.5学分 |
NXC3004 |
高等数学II |
5.5学分 |
NXC3002 |
线性代数 |
3.0学分 |
NXC3005 |
数学建模与计算 |
4.0学分 |
NXC3001 |
大学物理 |
5.0学分 |
(二)学科专业模块(共24门课程,86.0学分)
1. 学科基础课程(共2门课程,7.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
NXC4012 |
工程力学 |
3.5学分 |
NXC4008 |
工程设计方法 |
3.5学分 |
2. 专业核心课程(共22门课程,79.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
QXU4000 |
材料学I-结构与性能 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4006 |
材料学II-加工与应用 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4001 |
材料分子学 |
3.5学分 |
NXC4010 |
功能材料概论 |
3.5学分 |
QXU4011 |
工程材料概论 |
4.0学分 |
QXU4007 |
材料学实验I |
3.5学分 |
QXU5017 |
材料学实验II |
3.5学分 |
NXC4022 |
热力学与相变 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5002 |
材料化学 |
4.0学分 |
QXU5010 |
表面与界面 |
3.5学分 |
NXC5015 |
结构表征 |
3.5学分 |
NXC5026 |
金属I-变形与强化 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5030 |
复合材料 |
3.5学分 |
QXU5032 |
高分子材料物理性能 |
4.0学分 |
NXC5036 |
金属II-合金与热处理 |
3.5学分 |
QXU6002 |
材料设计与选择 |
4.0学分 |
QXU6007 |
材料的环境性能 |
3.5学分 |
QXU6022 |
陶瓷 |
4.0学分 |
NXC6023 |
疲劳与蠕变 |
3.0学分 |
NXC6024 |
断裂力学 |
3.0学分 |
NXC6025 |
制造技术 |
4.0学分 |
QXU7027 |
可再生能源材料 |
3.5学分 |
(三)综合素质模块(共6.0学分,至少4门课程,建议选修授课语言为英语的课程)
1.科学素养类课程:包含三航概论、环境、生物等自然科学,其中在“航空概论”、“航天概论”、“航海概论”课程中必须三选一;计算机基础课程必修。
2. 经管法类课程:包含经济、管理、法学等
3. 人文素养类课程:包含哲学、伦理、历史、文化、语言、文学、社会、审美、人生与发展等
4.艺术素养类课程:包含《艺术导论》、《音乐鉴赏》、《美术鉴赏》、《影视鉴赏》、《戏剧鉴赏》、《舞蹈鉴赏》、《书法鉴赏》、《戏曲鉴赏》等课程,其中《京剧艺术的呈现》课程必修。
建议学生选修英文授课课程,包含科学素养类课程、经管法类课程、人文素养类课程、艺术素养类课程四个模块,每学期开设的上述模块课程详见当学期选课手册。
(四)综合实践(共2门课程,9.0学分)
1. 毕业设计/论文(共1门课程,8.0学分)
课程编码 |
课程名称 |
学分 |
QXU6021 |
材料专业毕业设计 |
8.0学分 |
2. 科研训练(1.0学分)
包含创新创业项目、创新性实验项目、学科竞赛、高峰体验计划、科研实践类活动等。
并鼓励学生选择参与海外实习、课外实践、冬令营、夏令营等多种实践形式。
课程模块与学分分布表
课程模块 |
课程代码 |
课程名称 |
学时/ 学分 |
考核分配 |
学时分配 |
各学期学时分配 |
考试√ |
考查√ |
讲课 |
实验 (上机) |
一 1st |
二 2nd |
三 3rd |
四 4th |
五 5th |
六 6th |
七 7th |
八 8th |
通识通修 |
通识通修 |
NXC2001 |
思政课I-中国近代史纲要 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2002 |
思政课II-马克思主义基本原理 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
24 |
24 |
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2003 |
思政课II-思想道德修养与法律基础 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
24 |
24 |
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2004 |
思政课IV-毛泽东思想和中国特色社会主义理论体系概论 |
80/5.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
40 |
|
|
|
80/5.0 |
|
|
|
|
NXC2005 |
形势与政策 |
32/2.0 |
√ |
|
32 |
|
|
|
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
U34G11002 |
军事理论 |
32/2.0 |
√ |
|
32 |
|
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34P41001 |
军事技能训练 |
16/1.0 |
|
√ |
|
|
3周/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34G11001 |
大学生心理健康教育 |
8/0.5 |
√ |
|
8 |
|
在本科导师指导下学生按需自选 |
QXU3111 |
个人发展规划I |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4111 |
个人发展规划II |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
|
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
QXU5111 |
个人发展规划III |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
QXU3101 |
英语I |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU3102 |
英语II |
88/5.5 |
|
√ |
88 |
|
|
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71001 |
体育I |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71002 |
体育II |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71003 |
体育III |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71004 |
体育IV |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
NXC3000 |
高等数学I |
88/5.5 |
√ |
|
78 |
10 |
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3004 |
高等数学II |
88/5.5 |
√ |
|
88 |
|
|
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3001 |
大学物理 |
82/5.0 |
√ |
|
50 |
32 |
50/3.0 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3002 |
线性代数 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3005 |
数学建模与计算 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
24 |
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
小计 |
1122/66.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
学科专业 |
学科专业 |
NXC4012 |
工程力学 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
46 |
10 |
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
NXC4008 |
工程设计方法 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4000 |
材料学I-结构与性能 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4006 |
材料学II-加工与应用 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
QXU4001 |
材料分子学 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
NXC4010 |
功能材料概论 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4011 |
工程材料概论 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
16 |
24/1.5 |
40/2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4007 |
材料学实验I |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
|
56 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU5017 |
材料学实验I I |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
NXC4022 |
热力学与相变 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
QXU5002 |
材料化学 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
QXU5010 |
表面与界面 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
48 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
NXC5015 |
结构表征 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
NXC5026 |
金属I-变形与强化 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
QXU5030 |
复合材料 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
QXU5032 |
高分子材料物理性能 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
NXC5036 |
金属II-合金与热处理 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
QXU6002 |
材料设计与选择 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
QXU6007 |
材料的环境性能 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
QXU6022 |
陶瓷 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
NXC6023 |
疲劳与蠕变 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48/3.0 |
NXC6024 |
断裂力学 |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
NXC6025 |
制造技术 |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
54 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
QXU7027 |
可再生能源材料 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
小计 |
1376/86.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
综合素质(选修课程) |
综合素质(选修课程) |
NXC1001 |
京剧艺术的呈现 |
学生可在西北工业大学综合素养类课程清单及玛丽女王工程学院选修课清单中选修,每学期开设的上述课程详见当学期选课手册。 |
NXC1002 |
工笔画临摹与创作 |
NXC1003 |
走进国乐 |
U01L11001 |
航空概论 |
U02L11001 |
航天概论 |
U03L11001 |
航海概论 |
NXC1004 |
计算机基础 |
NXC1005 |
无机化学 |
NXC1006 |
基础有机化学 |
NXC1007 |
物理化学 |
NXC1008 |
3D打印 |
…… |
…… |
|
小计 |
96/6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
综合实践 |
综合实践 |
QXU6021 |
材料专业毕业设计 |
128/8.0 |
|
√ |
|
128 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
128/8.0 |
|
科研训练 |
16/1.0 |
在本科导师指导下学生参加 |
|
小计 |
144/9.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
总学时/学分合计:2738/167.0 |
附注说明:课程代号QX为英方教师授课,NX为中方教师英文授课,U为教育部规定必修中文授课的军事理论课程及部分中文选修课程等 |
八、教学模式
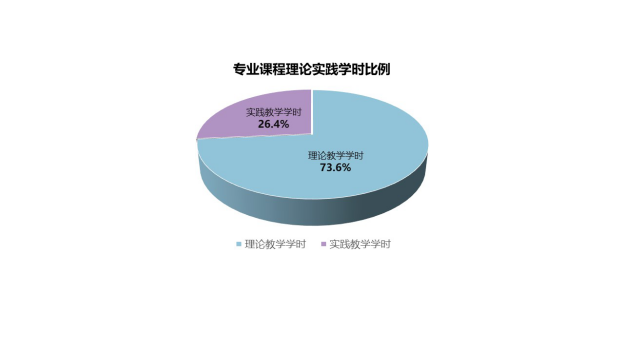
借鉴英国高等教育培养创新型本科人才的先进理念,除思政和体育以外的所有课程均采用多元化授课模式,融合理论教学、课堂实验、案例学习、综合运用、开放实验等多种教学方法,由“讲3、学2、考1”的传递-接受式教学向“讲1、学2、考3”的自学-辅导式教学转变,重点培养学生自学、问题解决和动手实践的能力,激发学生的内在动力,挖掘其对知识的兴趣,培养学生终身学习能力和工作能力。
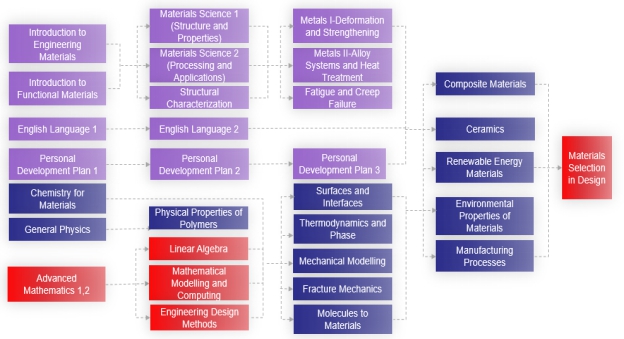
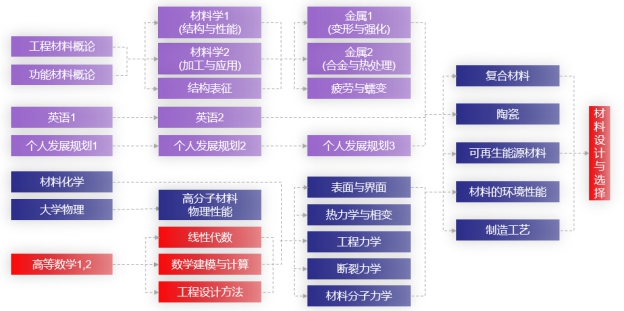
九、课程逻辑关系图
专业课程设置体系以“培养具有国际视野、通晓国际规则,具有坚实的自然科学基础、材料科学与工程专业基础和人文基础,专业竞争力强、综合素质高,能够进行跨国学习、工作并具备终生学习能力的复合型创新人才”的人才培养目标为依据,将主要课程分别归入几大课程模块之中,课程之间相互支持与衔接,突出专业特色,满足专业学术型、交叉复合型、就业创业型人才培养要求。主要课程逻辑关系图如下:
MaterialsScience and Engineering
Education Programme for Undergraduates
(QMUL Engineering School)
1.ProgrammeIntroduction
Materials are the basic necessity of human existence. Materials science and engineeringis the foundation of science, technology, and manufacturing. As a syncretic discipline hybridizing materials science, engineering, physics, and chemistry, materials science and engineering builds the foundation of aviation, marine engineering, new energy, information technology, renewable resources, and intelligent manufacturing. Materials discipline, which covers metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites, is one of the most influential and distinct disciplines in Queen Mary University of London (hereinafter as QMUL). The Materials programme of QMUL provideselite education and professional training for students with a thorough grounding in the structure of materials, the properties of materials, the performance of materials and the manufacturing processes and design. The discipline has been rated as 5-star by the British government many times. A survey conducted by the National Union of Students in 2011 showed that it ranked top 1 in the UK. The Materials programmes in Northwestern Polytechnical University (hereinafter as NPU) enjoy a high reputation and a great popularity internationally. Materials Science and Engineering of NPU is the National Key Discipline and ranked top 3 among all National Key Disciplines in the 2012 Discipline Evaluation in China. NPU also has 6 scientific research and talent-training platforms at national level.
Approved by the Ministry of Education of China, NPU and QMUL have launched a joint educational institutionnamed Queen Mary University of London Engineering School, Northwestern Polytechnical University (hereinafter referred to as JEI), in order to provide Chinese students with typical British education that emphasises on developing undergraduate students’ innovation ability. The JEI, which builds on the acknowledged expertise and experience of the two universities and their complementary research strengths in materials science, fully uses educational resource advantages and high-level international cooperation platforms of both universities to provide a high quality degree level education in the programme of Materials Science and Engineering (080401H). The programme draws on the academic expertise of both institutions and adopts an international teaching mode with curriculum system, teaching materials, and assessment methods from the UK. The mission of this programme is to develop qualified and innovative talents who can study and work transnationally with the knowledge of natural science, materials science and engineering, and social science. Students graduate with comprehensive qualities, high professional competencies, a global horizon, a life-long study ability, and recognition of international rules.
2. Educational Aims
Under the guidance of Marxism, this programme aims to enhance morality and foster talents, to develop qualified and innovative talents who can study and work transnationally with the knowledge of natural science, materials science and engineering, and social science. Students graduate with comprehensive qualities, high professional competencies, a global horizon, a life-long study ability, and the recognition of international rules. Students who have completed their studies will be able to pursue higher degrees and research within universities in China and internationally or careers in the expanding materials science and manufacturing industry in world famous enterprises.
(1)Be equipped with solid basic knowledge and professional skills
Students should master basic principles in materials science and engineering, experimental and computing methods in the field of engineering and materials science, and knowledge of material design and making, material forming and shaping, product design, and application development. Students should be equipped with the ability to research and analyse the structure, the properties and the performance of metallic materials, inorganic nonmetallic materials, composite materials, and advanced materials. Students are able to solve technical problems in their professional field.
(2)Be equipped with international competitiveness
Students become highly proficient in English language: reading English materials and books in materials science, writing academic essays in English, and conducting technical presentations in English. The programme develops students’ global horizon and the recognition of international rules via the British teaching mode and overseas internship programme. Students can obtain, use and manage various information to conduct cross-cultural communication and cooperation with innovative abilities and international competitiveness. Students can recognize Chinese characteristics and international comparisons correctly, as well as comprehend modern China and the world objectively and comprehensively.
(3)Be equipped with the ability of life-long study
Students should stick to Marxist theory, promote and practice Socialist Core Values, recognize the responsibility of times and mission of history, and to understand ambition and dedication correctly. Students should have a strong sense of social responsibility, a healthy mental and moral state, the ability of leading and working in teams, and outstanding communicative and practical skills. Equipped with good presentation skills and writing abilities, students can communicate effectively with their peers and the public about complex engineering and scientific problems. The cultivation of consciousness of engineering ethics, and the concept of working for the wellbeing of the human beings and sustainable development can help students to adapt to dynamic changes, and master the cutting-edge knowledge and new trends in the field of materials science so as to constantly improve students’ abilities.
3. Educational Requirements
(1)Master basic knowledge
Students should master: extensive knowledge in the field of materials science including materials science and engineering, the structure of materials, the properties of materials, the performance of materials, the manufacturing processes and design, and application and development; intensive professional knowledge, including surfaces and interfaces, materials chemistry, polymer materials, ceramic materials, renewable materials, and sustainable development; experimental and computational methods in the field of engineering and materials science.
(2)Develop professional skills
Students should be equipped with creative problem-solving and transferable skills and recognize the important value of materialsscience to engineering and other technologies. On the premise of safety, students conduct various experiments practically and are able to design, conduct, analyze and evaluate experiments and the results. Theoretically, students are familiar with the operation of all kinds of equipment used in experiments, tests, and analysis and are capable of searching, collecting and selecting data and presenting scientific and technical report. At last, students should have related abilities to conduct scientific research and develop technology and products.
(3)Develop comprehensive qualities
Students should have the abilities of international competitiveness, communication, life-long study, independent study and work, and leading and working in teams. Students can estimate the relevance, importance and reliability of various information and realize the influence of science and engineering on the future of the society worldwide. Students are capable of computing, analyzing and managing data, and communicating and cooperating transnationally with innovative ability and international competitiveness. With the concept of sustainable development in mind, students are exposed to cutting-edge technology changes in the field of materials and can improve themselves constantly in practice.
4. Qualification and Degree Certificate
Official length of the programme: 4+0 years’ study in accordance with the credit management system.
Qualification and certificate: Successful students of the programme will be awarded diploma by NPU, BEng degree by NPU, and BEng degree by QMUL.
5. Fundamental Credits/ Hours
MaterialsScience and Engineering(080401H), total modules 52, credits 167.0, teaching hours 2738, detailed credits and hours as follows:
Module |
Credit |
Hour |
Language |
General Education |
66.0 |
1122 |
Chinese/English |
Discipline |
86.0 |
1376 |
English |
Comprehensive Literacy |
6.0 |
96 |
Chinese |
Comprehensive Practices |
9.0 |
144 |
English |
6. Discipline Module
MaterialsScience and Engineering(080401H) discipline module, total modules 24, credits 86.0/1376, detailed modules as follows:
A. Discipline elementary modules (2 modules, 7.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
NXC4012 |
Mechanical Modelling |
3.5 credits |
NXC4008 |
Engineering Design Methods |
3.5 credits |
B. Discipline core modules (22 modules, 79.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
QXU4000 |
MSI-Structure and Properties |
3.5 credits |
QXU4001 |
Molecules to Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU4006 |
MS II-Processing and Applications |
3.5 credits |
NXC4010 |
Introduction to Functional Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU4011 |
Introduction to Engineering Materials |
4.0 credits |
QXU4007 |
Experiments in Materials 1 |
3.5 credits |
QXU5017 |
Experiments in Materials 2 |
3.5 credits |
NXC4022 |
Thermodynamics and Phase Transformations |
3.5 credits |
QXU5002 |
Chemistry for Materials |
4.0 credits |
QXU5010 |
Surfaces and Interfaces |
3.5 credits |
NXC5015 |
Structural Characterisation |
3.5 credits |
NXC5026 |
Metals I-Deformation and Strengthening |
3.5 credits |
QXU5030 |
Composite Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU5032 |
Physical Properties of Polymers |
4.0 credits |
NXC5036 |
Metals II-Alloy Systems and Heat Treatment |
3.5 credits |
QXU6002 |
Materials Selection in Design |
4.0 credits |
QXU6007 |
Environmental Properties of Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU6022 |
Ceramics |
4.0 credits |
NXC6023 |
Fatigue and Creep Failure |
3.0 credits |
NXC6024 |
Fracture Mechanics |
3.0 credits |
NXC6025 |
Manufacturing Processes |
4.0 credits |
QXU7027 |
Renewable Energy Materials |
3.5 credits |
7. Curriculum Modules and Credits, total52 modules,167.0 credits
There are 4 modules in this major, as:
◆General education module : 22 modules, 66.0 credits/ 1122 hours;
◆Discipline module: 24 modules, 86.0 credits/ 1376 hours;
◆Comprehensive literacy module: at least 4 modules, 6.0 credits/ 96hours;
◆Comprehensive practices module : 2 modules, 9.0 credits/ 144 hours;
Except for Ideological and political theory modules, Military modules, Mental Health Education module and PE modules (23.5 credits), 79.0 credits are QMUL taught modules, 64.5 credits are NPU taught modules, and20 introduced modules are English Language, PDP, 14 discipline core modules and major project, partially satisfying the requirement ofRegulations of the People’s Republic of China on Chinese-Foreign Cooperation in Running Schoolsand MoE relative rules, which are:
◆numbers of introduced modules (20) take 39.2% of numbers of total modules (52)(over 1/3);
◆numbers of introduced major core modules (14) take 63.6% of numbers of total major modules (22) (over 1/3);
◆numbers of QMUL teaching major core modules (14) take 27.5% of numbers of total modules (52);
◆class hours of QMUL teaching major core modules (824) take 30.1% of class hours of total modules (2738).
(1) General education modules (22 modules, 66.0 credits)
A. Ideological and political theory modules (5 modules, 16.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
NXC2001 |
Chinese compulsory courses I-Essentials of Chinese Modern History |
3.0 credits |
NXC2002 |
Chinese compulsory courses II-Marxism General Principle |
3.0 credits |
NXC2003 |
Chinese compulsory courses III-Ethics and Fundamental of Law |
3.0 credits |
NXC2004 |
Chinese compulsory courses IV-Fundamental of Mao Ze Dong Thoughts |
5.0 credits |
NXC2005 |
Situation and Policy |
2.0 credits |
B. Military modules (2 modules, 3.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
U34G11002 |
Military Theory |
2.0 credits |
U34P41001 |
Military Training |
1.0 credit |
C. Mental growth and personal development modules (1 module, 0.5 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
U34G11001 |
Students Mental Health Education |
0.5 credit |
D. Career planning and development modules (3 module, 10.5 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
QXU3111 |
PDP I |
3.5 credits |
QXU4111 |
PDP II |
3.5 credits |
QXU5111 |
PDP III |
3.5 credits |
E. University general education modules (6modules, 13.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
QXU3101 |
English Language I |
3.5 credits |
QXU3102 |
English Language II |
5.5 credits |
Physical Education is compulsory module in the first to the fourth semester, taking 1 credit every semester. Students can freely choose different module according to their majors, physical conditions, interesting and physical basis.
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
U31G71001 |
Physical educationI |
1.0 credit |
U31G71002 |
Physical educationII |
1.0 credit |
U31G71003 |
Physical educationIII |
1.0 credit |
U31G71004 |
Physical educationIV |
1.0 credit |
F. Level-based general education modules (5 modules, 23.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
NXC3000 |
Advanced Maths I |
5.5 credits |
NXC3004 |
Advanced Maths II |
5.5 credits |
NXC3002 |
Linear Algebra |
3.0 credits |
NXC3005 |
Mathematical Modelling and Computing |
4.0 credits |
NXC3001 |
General Physics |
5.0 credits |
(2) Discipline Modules (24 modules, 86.0 credits)
A. Discipline elementary modules (2 modules, 7.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
NXC4012 |
Mechanical Modelling |
3.5 credits |
NXC4008 |
Engineering Design Methods |
3.5 credits |
B. Discipline core modules (22 modules, 79.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
QXU4000 |
MS I-Structure and Properties |
3.5 credits |
QXU4006 |
MS II-Processing and Applications |
3.5 credits |
QXU4001 |
Molecules to Materials |
3.5 credits |
NXC4010 |
Introduction to Functional Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU4011 |
Introduction to Engineering Materials |
4.0 credits |
QXU4007 |
Experiments in Materials 1 |
3.5 credits |
QXU5017 |
Experiments in Materials 2 |
3.5 credits |
NXC4022 |
Thermodynamics and Phase Transformations |
3.5 credits |
QXU5002 |
Chemistry for Materials |
4.0 credits |
QXU5010 |
Surfaces and Interfaces |
3.5 credits |
NXC5015 |
Structural Characterisation |
3.5 credits |
NXC5026 |
Metals I-Deformation and Strengthening |
3.5 credits |
QXU5030 |
Composite Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU5032 |
Physical Properties of Polymers |
4.0 credits |
NXC5036 |
Metals II-Alloy Systems and Heat Treatment |
3.5 credits |
QXU6002 |
Materials Selection in Design |
4.0 credits |
QXU6007 |
Environmental Properties of Materials |
3.5 credits |
QXU6022 |
Ceramics |
4.0 credits |
NXC6023 |
Fatigue and Creep Failure |
3.0 credits |
NXC6024 |
Fracture Mechanics |
3.0 credits |
NXC6025 |
Manufacturing Processes |
4.0 credits |
QXU7027 |
Renewable Energy Materials |
3.5 credits |
(3) Comprehensive literacy modules (6.0 credits, at least 4 modules, students are suggested to choose English taught modules)
A. Scientific literacy modules:subjects on natural science such as introduction to aeronautics, astronautics and navigation, environment, biology, etc. Students must take one module among “An Introduction to Aviation”, “An Introduction to Astronautics”, and “An Introduction to Marine Navigation”. Computer fundamentals are a compulsory module.
B. Modules on economics, management and law:including economy, management, legal education, etc.
C. Humanities modules:including philosophy, ethics, history, culture, language, literature, society, aesthetics, life and development, etc.
D. Art literacy modules:students can choose modules form “An Introduction to Art”, “Music Appreciation”, “Art Appreciation”, “Film Appreciation”, “Drama Appreciation”, “Dance Appreciation”, “Calligraphy Appreciation”, and “Chinese Opera Appreciation”, among which “The Presentation of the Art of Peking Opera” is compulsory.
It issuggestedthat students should choose English taught modules, from all four categories above. Each module offered in each semester will be included in the course selection manual.
(4) Comprehensive practices (2 modules, 9.0 credits)
A. Design for graduation (1 module, 8.0 credits)
Module Code |
Module Name |
Credit |
QXU6021 |
Materials Project |
8.0 credits |
B. Scientific research project modules(1.0 credit)
Students can participate in a variety forms of scientific research training including innovative research programmes, academic competition, innovative and business training plan for college students, academic competitions, “Peak Experience Plan”, social research, and scientific research project. Students are encouraged to participate in a variety forms of central practice such as overseas practice, international internship, winter and summer camp.
Curriculum Modules and Credits Table
Module |
Code of Course |
Name of Course |
Credit/ Hour |
Test Approach |
Hour Distribution |
Hour Distribution for Semesters |
Exam√ |
Test√ |
Teach |
Practice (Computer) |
1st |
2nd |
3rd |
4th |
5th |
6th |
7th |
8th |
General education |
General education |
NXC2001 |
Chinese Compulsory Modules I Essentials of Chinese Modern History |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2002 |
Chinese Compulsory Modules II Marxism General Principle |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
24 |
24 |
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2003 |
Chinese Compulsory Modules III Ethics and Fundamental of Law |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
24 |
24 |
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC2004 |
Chinese Compulsory Modules IVFundamental of Mao Ze Dong Thoughts |
80/5.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
40 |
|
|
|
80/5.0 |
|
|
|
|
NXC2005 |
Situation and Policy |
32/2.0 |
|
√ |
32 |
|
|
|
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
U34G11002 |
Military Theory |
32/2.0 |
√ |
|
32 |
|
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34P41001 |
Military Training |
16/1.0 |
|
√ |
|
|
3w/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34G11001 |
Students Mental Health Education |
8/0.5 |
√ |
|
8 |
Select under the guidance of tutor |
QXU3111 |
PDP I |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4111 |
PDP II |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
|
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
QXU5111 |
PDP III |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
24/1.5 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
QXU3101 |
English Language I |
56/3.5 |
|
√ |
56 |
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU3102 |
English Language II |
88/5.5 |
|
√ |
88 |
|
|
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34G11002 |
Physical Education I |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
32 |
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
U34P41001 |
Physical Education II |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
32 |
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71001 |
Physical Education III |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
32 |
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
U31G71002 |
Physical Education IV |
32/1.0 |
√ |
|
|
32 |
|
|
|
32/1.0 |
|
|
|
|
NXC3000 |
Advanced Maths I |
88/5.5 |
√ |
|
78 |
10 |
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3004 |
Advanced Maths II |
88/5.5 |
√ |
|
88 |
|
|
88/5.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3001 |
General Physics |
82/5.0 |
√ |
|
50 |
32 |
50/3.0 |
32/2.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3002 |
Linear Algebra |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
|
48/3.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
NXC3005 |
Mathematical Modelling and Computing |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
24 |
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
1122/66.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Discipline |
Discipline |
NXC4012 |
Mechanical Modelling |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
46 |
19 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
NXC4008 |
Engineering Design Methods |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4000 |
MS I Structure and Properties |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4006 |
MS II Processing and Applications |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
QXU4001 |
Molecules to Materials |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
NXC4010 |
Introduction to Functional Materials |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4011 |
Introduction to Engineering Materials |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
16 |
24/1.5 |
40/2.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
QXU4007 |
Experiments in Materials 1 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
|
56 |
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
QXU5017 |
Experiments in Materials 2 |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
NXC4022 |
Thermodynamics and Phase Transformations |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
|
QXU5002 |
Chemistry for Materials |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
QXU5010 |
Surfaces and Interfaces |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
48 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
NXC5015 |
Structural Characterisation |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
NXC5026 |
Metals I Deformation and Strengthening |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
|
QXU5030 |
Composite Materials |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
QXU5032 |
Physical Properties of Polymers |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
|
|
NXC5036 |
Metals II Alloy Systems and Heat Treatment |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
40 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
|
QXU6002 |
Materials Selection in Design |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
48 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
QXU6007 |
Environmental Properties of Materials |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
QXU6022 |
Ceramics |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
56 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
NXC6023 |
Fatigue and Creep Failure |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48/3.0 |
NXC6024 |
Fracture Mechanics |
48/3.0 |
√ |
|
40 |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
48/3.0 |
|
NXC6025 |
Manufacturing Processes |
64/4.0 |
√ |
|
54 |
10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
64/4.0 |
|
QXU7027 |
Renewable Energy Materials |
56/3.5 |
√ |
|
56 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
56/3.5 |
|
Total |
1376/86.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive literacy (Elective courses) |
Comprehensive literacy |
NXC1001 |
The Presentation of the Art of Peking Opera |
NPU and QMES elective courses are available for students, including comprehensive development courses. Each semester courses can be checked on course-election handbook. |
NXC1002 |
The Copy and Creation of Traditional Chinese Realistic Painting |
NXC1003 |
An Introduction to Classical Music of China |
U01L11001 |
An Introductionto Aviation |
U02L11001 |
An Introduction to Astronautics |
U03L11001 |
An Introduction to Marine Navigation |
NXC1004 |
Fundamentals of Computer |
NXC1005 |
Inorganic Chemistry |
NXC1006 |
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry |
NXC1007 |
Physical Chemistry |
NXC1008 |
3D Print |
… |
… |
|
Total |
96/6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Comprehensive practice |
Comprehensive practice |
QXU6021 |
MaterialProject |
128/8.0 |
|
√ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
128/8.0 |
|
Scientific Research |
16/1.0 |
Participate under the guidance of tutor |
|
Total |
144/9.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total hours / total credits 2738/167.0 |
Reference: Code QX courses are taught by QMUL. Code NX courses are taught by NPU. Code U courses are Chinese Compulsory Courses, Mental Health, Military Theory courses from MoE, as well as some elective courses. |
8. Mode of Teaching
Taking theuseof Britain’s high education concept to cultivate innovative bachelor talents for reference, multiple education modes are practiced, such as theory teaching, experiment teaching, case study, comprehensive application and open-experimental instruction, in all modules except for Chinese Compulsory and PE courses. Rather than relying on the traditional reception teaching, we adopt the student-centred teaching mode, which highlights on fostering students’ ability of self-study, problem-solving and hands-on practice. JEI programmes intend to motivate students’ inner impetus, discover their interests for knowledge and cultivate their lifelong learning as well as working ability.
9. Curriculum Logical Diagram
In accordance with the aim “to develop qualified and innovative talents who can study and work transnationally with the knowledge of natural science, materials science and engineering, and social science. Students graduate with comprehensive qualities, high professional competencies, a global horizon, a life-long study ability, and the recognition to international rules”, major courses are divided into several modules, support and linked with each other, emphasizing on principle specialty, meeting the education standard of professional, composite and entrepreneurial talents.